
<상속 문법 예제>
1.python
# 부모 클래스
class Animal:
def eat(self):
print("Eating...")
# 자식 클래스
class Cat(Animal):
def meow(self):
print("Meow!")
cat = Cat()
cat.eat() # "Eating..." 출력
cat.meow() # "Meow!" 출력2.java
// 부모 클래스
public class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Eating...");
}
}
// 자식 클래스
public class Cat extends Animal {
public void meow() {
System.out.println("Meow!");
}
}
// 메인 클래스
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.eat(); // "Eating..." 출력
cat.meow(); // "Meow!" 출력
}
}3.javascript
// 부모 클래스
class Animal {
eat() {
console.log("Eating...");
}
}
// 자식 클래스
class Cat extends Animal {
meow() {
console.log("Meow!");
}
}
const cat = new Cat();
cat.eat(); // "Eating..." 출력
cat.meow(); // "Meow!" 출력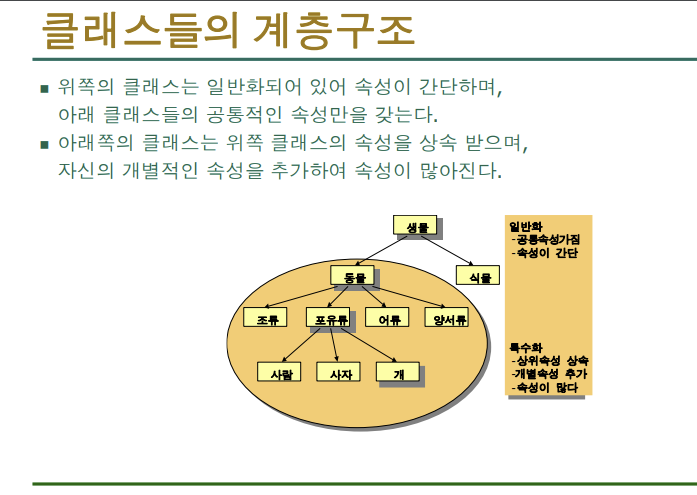
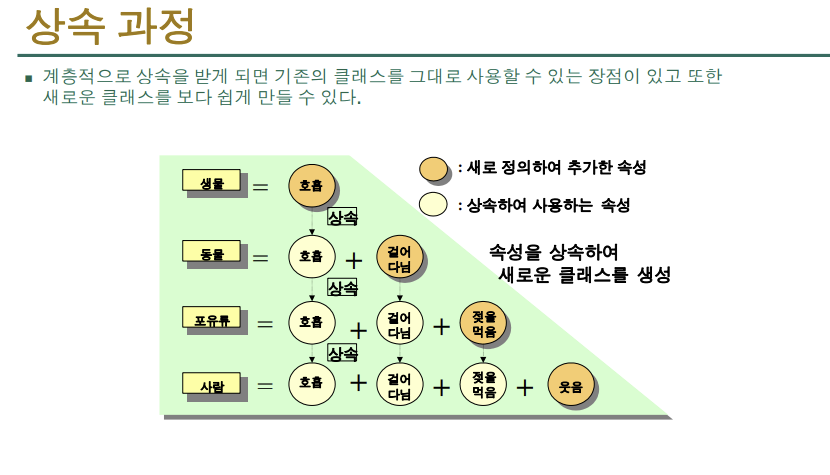
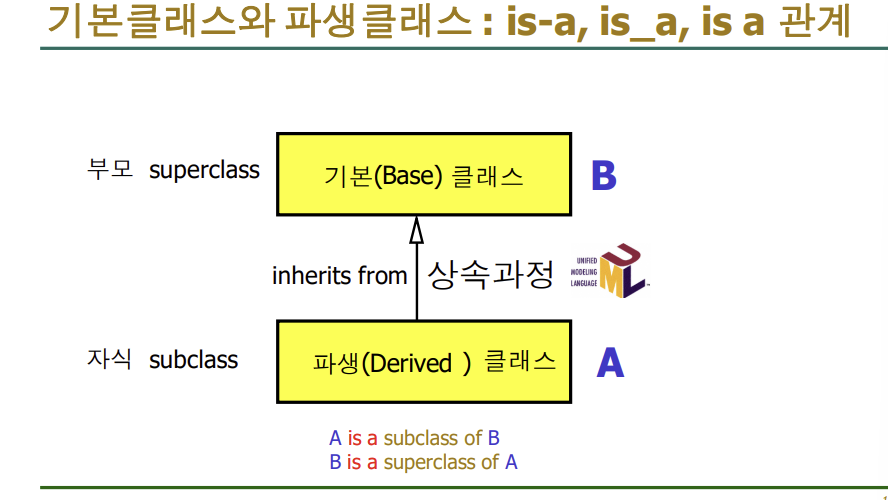
- 상속은 부모 자식간의 관계 : 멋있게(?) 말할때는 is a관계라고 한다
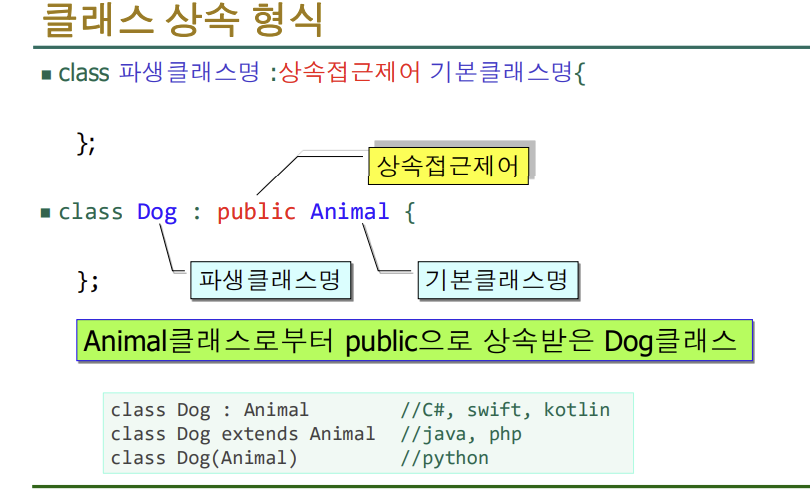
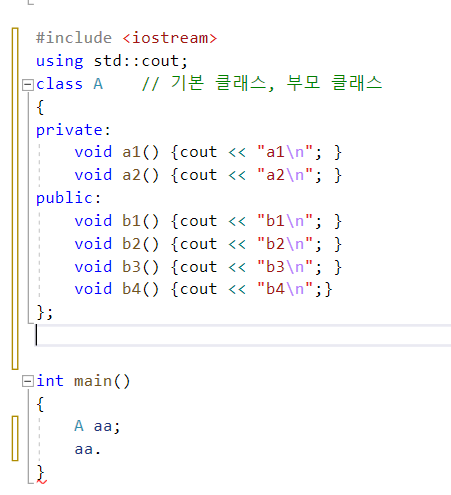
private를 제외하고 모두 물려 받는다
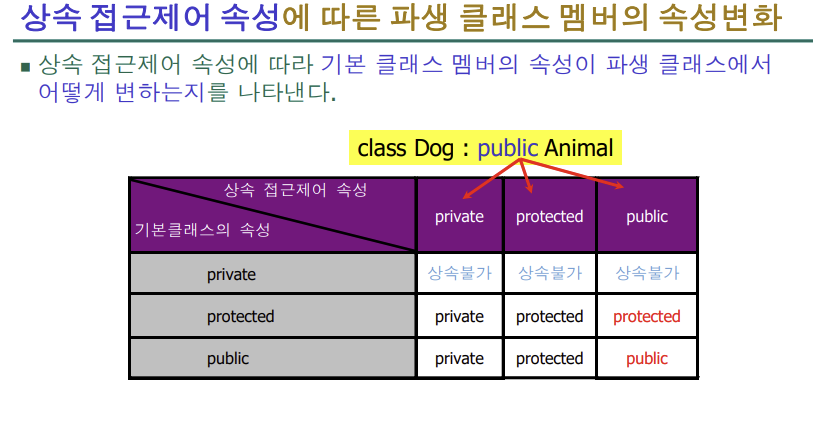
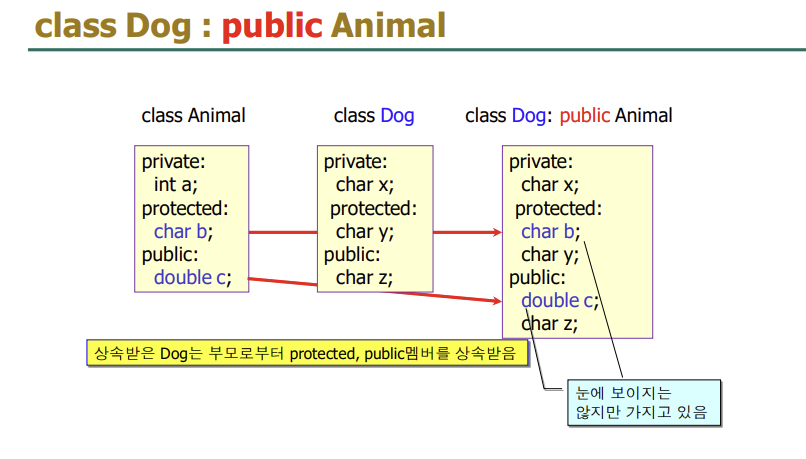
부모의 protected와 public이 그대로 자식에게 돌아온다
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class A // 기본 클래스
{
int x;//생략가능
public:
void setX (int i) {x =i;}
void showX() { cout << x << endl; }
};
class B:public A //파생 클래스
{
//아무 것도 없어요. 그러나!
};
int main() {
A aa;
aa.setX(1);
aa.showX(); B bb;
bb.setX(10);
bb.showX();
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class A // 기본 클래스 A 선언
{
int x; // private 멤버 변수 x
public:
void setX(int i) { x = i; } // x에 값을 설정하는 public 멤버 함수
void showX() { cout << x << endl; } // x의 값을 출력하는 public 멤버 함수
};
class B :public A // A 클래스를 상속받는 파생 클래스 B 선언
{
int y; // private 멤버 변수 y
public:
void setY(int i) { y = i; } // y에 값을 설정하는 public 멤버 함수
void showY() { cout << y << endl; } // y의 값을 출력하는 public 멤버 함수
};
int main()
{
B bb; // B 클래스의 객체 bb 생성
bb.setX(1); // bb 객체의 x값을 1로 설정 (A 클래스의 메서드 이용)
bb.setY(2); // bb 객체의 y값을 2로 설정 (B 클래스의 메서드 이용)
bb.showX(); // bb 객체의 x값 출력 (A 클래스의 메서드 이용)
bb.showY(); // bb 객체의 y값 출력 (B 클래스의 메서드 이용)
return 0;
}
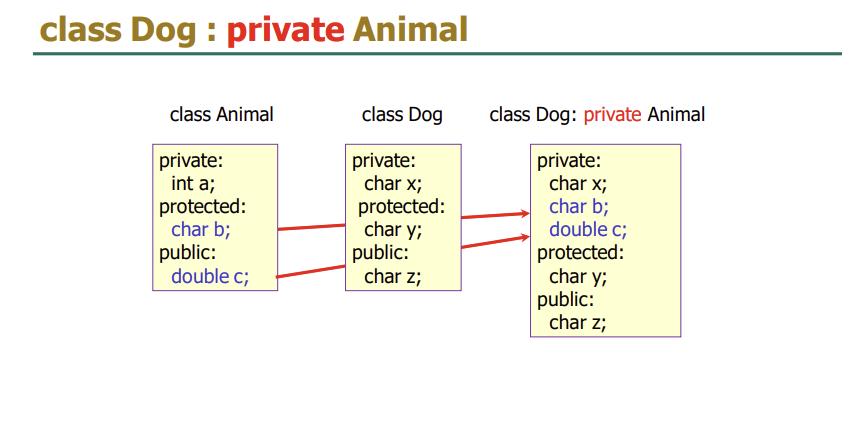
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class A
{
int x;//private 생략 가능
public:
void setX(int i) { x = i; }
void showX() { cout << x << endl; }
};
class B :public A
{
int y;
public:
void setY(int i) { y = i; }
void
showXY() { showX(); cout << y << endl; }
};
int main()
{
B bb;
bb.setX(1); // 기본클래스의 멤버접근
bb.setY(2); // 파생클래스의 멤버접근
bb.showX(); // 기본클래스의 멤버접근
bb.showXY(); // 파생클래스의 멤버접근
return 0;
}In-class member initializers:클래스 안에서 멤버 변수를 바로 초기화하는 방법
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class A
{
int x = 1;
public:
A() { x = 2; } //(=A():x(2){})
void setX(int i) { x = i; }
int getX() { return x; }
};
int main()
{
A a1; //디폴트 생성자는 사라짐
cout << a1.getX() << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class A
{
int x;
public:
void setX(int i) { x = i; }
void showX() { cout << x << endl; }
};
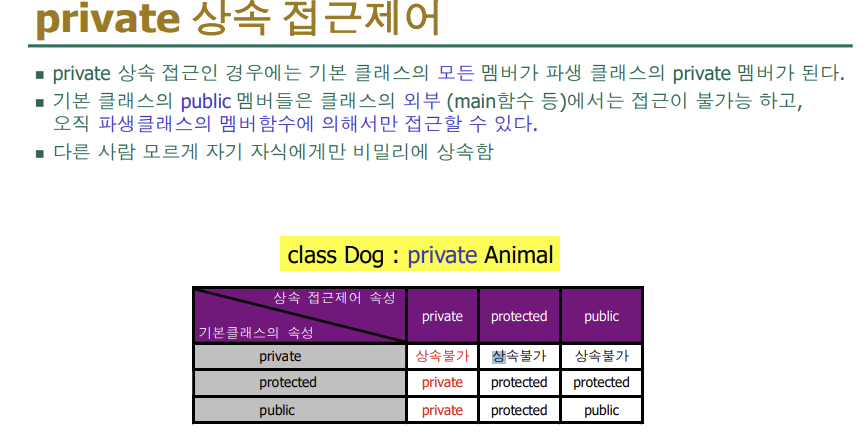
class B :private A //비공개적으로 상속받는다/ 자식만 사용가능, 그래서 setX와 ShowX를 사용
{
int y;
public:
void setXY(int i, int j) { setX(i); y = j; }
// 기본 클래스의 public 멤버 접근
void showXY() { showX(); cout << y << endl; }
};
int main()
{
B bb;
bb.setXY(1, 2); // 파생클래스의 멤버접근
bb.showXY(); // 파생클래스의 멤버접근
return 0;
}protected부분이 없으면 private부분으로 상속된다
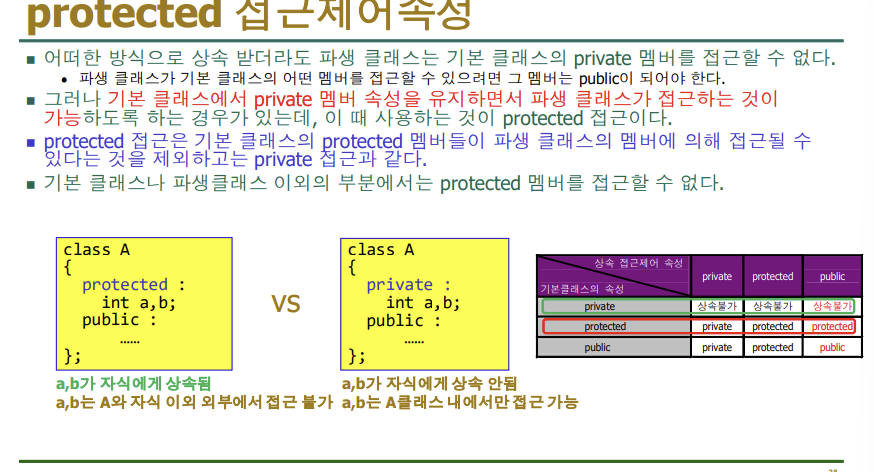
protected, private공통점 외부에서 둘다 접근 불가
차이점: protected는 자식에게 상속가능, private는 자식에게 상속 불가

-부모에서는 항상 private를 썼는데 자식에게 물려줄려면 protected를 사용하는 것이 좋다
-생성자는 부모꺼먼저 그리고 자식
-소멸자는 자식먼저 호출이 되고 부모

#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class A //할아버지
{
int a;
public:
A(int i) { a = i; }
int getA() { return a; }
};
class B :public A //아버지
{
int b;
public:
B(int i, int j) :A(i) {
// i는 기본 클래스 A의
//생성자 매개변수로 전달됨
b = j;
}
int getB() { return b; }
};
class C :public B //자식
{
int c;
public:
C(int i, int j, int k) :B(i, j) {
// i, j는 클래스 B의 생성자 매개변수로 전달됨
c = k;
}
void show() {
cout << getA() << ' ' << getB() << ' ' << c << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
C cc(10, 20, 30);
cc.show();
cout << cc.getA() << ' ' << cc.getB() << endl;
return 0;
}다중상속의 접근 방식이 public상속
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class A
{
protected: //private이라면?
int a, b;
public:
void setAB(int i, int j) { a = i; b = j; }
};
class B :public A
{
int c; // private
public:
void setC(int n) { c = n; }
void showABC() { cout << a << b << c << endl; }
//기본 클래스의 protected 멤버들은
//파생 클래스의 멤버에 의해 접근될 수 있다.
};
int main()
{
A aa;
B bb;
aa.a; //외부에서는 접근불가
bb.b; //외부에서는 접근불가
bb.setAB(1, 2);
bb.setC(3);
bb.showABC();
return 0;
}출처: 1학년 2학기 수업자료/ 한성현 교수님
'C++프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| c++프로그래밍 15주차 과제 (0) | 2023.12.13 |
|---|---|
| C++프로그래밍 13주차 과제 (1) | 2023.11.29 |
| C++프로그래밍 11주차 과제 (0) | 2023.11.15 |
| c++프로그래밍 10주차 과제 (1) | 2023.11.08 |
| C++ 프로그래밍 9주차 과제 (1) | 2023.11.01 |
